Spinal Problem:
Navigating Spinal Cord Compression: Understanding, Treatment, and Prevention
- By Abhishek --
- Friday, 10 May, 2024
Understanding Spinal Cord Compression: Causes, Symptoms, and Prevention:
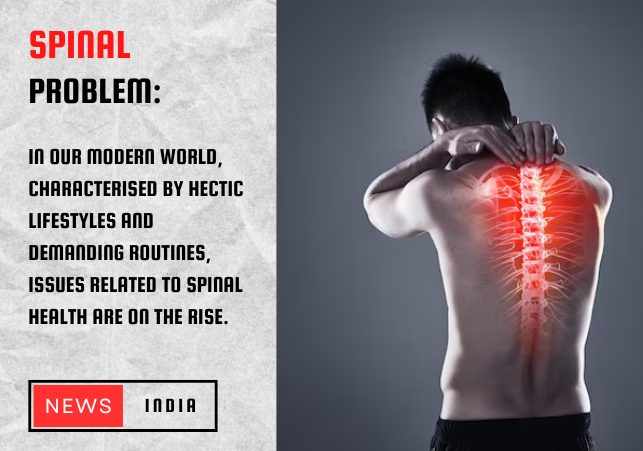
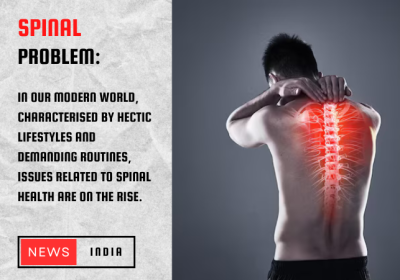
In our modern world, characterised by hectic lifestyles and demanding routines, issues related to spinal health are on the rise. The spine, a crucial component of our body's anatomy, serves as the bridge between our brain and the rest of our body. However, when this vital connection is disrupted, even simple tasks like walking can become arduous. One prevalent issue that arises from such disruption is spinal cord compression.
Spinal cord compression, often colloquially referred to as pressure on the backbone, occurs when there is undue pressure exerted on the spinal cord. This pressure interferes with the normal functioning of the nerves and tissues that make up the spinal cord, leading to a cascade of symptoms that can significantly impact one's quality of life. From pain and stiffness to difficulty walking and even urinary or faecal incontinence, the symptoms of spinal cord compression can vary widely and manifest in different parts of the body, making even the simplest tasks a challenge.
Understanding the causes of spinal cord compression is essential for effective prevention and management. Several factors can contribute to this condition, including abnormal alignment of the spine, injuries to the backbone, spinal tumours, bone diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, and infections. Identifying the underlying cause is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment.
Diagnosing spinal cord compression typically involves a series of medical tests, including spine X-rays, CT scans, and MRI tests. These diagnostic tools help healthcare professionals assess the extent of the compression and formulate a tailored treatment plan. Early diagnosis and tailored treatment are crucial for managing spinal cord compression, empowering individuals to take control of their spinal health.
Treatment options for spinal cord compression range from medication to surgical interventions, depending on the severity of the condition. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and steroids may be prescribed to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, radiation therapy, physical therapy, acupuncture, or cryoprotection may be recommended to manage symptoms and improve mobility.
However, as the adage goes, prevention is better than cure. Adopting proactive measures to maintain spinal health can significantly reduce the risk of spinal cord compression. Simple lifestyle changes such as daily exercise, maintaining proper posture, controlling weight, following a balanced diet, and avoiding smoking can all contribute to spinal health and overall well-being.
It's important to note that while the information provided here is based on media reports, consulting with a qualified healthcare professional is imperative before implementing any preventive measures or treatment options. Each individual's condition is unique, and a personalised approach is necessary for the effective management of spinal cord compression.
In conclusion, spinal cord compression is a severe condition that can have profound implications for one's health and mobility. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and preventive measures associated with this condition, individuals can take proactive steps to safeguard their spinal health and enjoy a better quality of life.


.png)